The awk command is a powerful tool in Linux for processing and analyzing text files, which is particularly useful when you need to perform arithmetic operations within loops.
This article will guide you through using awk for arithmetic operations in loops, using simple examples to make the concepts clear.
What is awk?
awk is a scripting language designed for text processing and data extraction, which reads input line by line, splits each line into fields, and allows you to perform operations on those fields. It’s commonly used for tasks like pattern matching, arithmetic calculations, and generating formatted reports.
The basic syntax of awk is:
awk 'BEGIN { initialization } { actions } END { finalization }' file
BEGIN: Code block executed before processing the input.actions: Code block executed for each line of the input.END: Code block executed after processing all lines.
Performing Arithmetic Operations in Loops
Let’s explore how to use awk to perform arithmetic operations within loops with the following useful examples to demonstrate key concepts.
Example 1: Calculating the Sum of Numbers
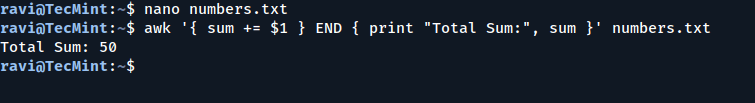
Suppose you have a file named numbers.txt containing the following numbers:
5 10 15 20
You can calculate the sum of these numbers using awk:
awk '{ sum += $1 } END { print "Total Sum:", sum }' numbers.txt
Explanation:
{ sum += $1 }: For each line, the value of the first field$1is added to the variablesum.END { print "Total Sum:", sum }: After processing all lines, the totalsumis printed.
Example 2: Calculating the Average
To calculate the average of the numbers:
awk '{ sum += $1; count++ } END { print "Average:", sum / count }' numbers.txt
Explanation:
count++: Increments the counter for each line.sum / count: Divides the total sum by the count to calculate the average.

Example 3: Multiplication Table
You can use awk to generate a multiplication table for a given number. For example, to generate a table for 5:
awk 'BEGIN { for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) print "5 x", i, "=", 5 * i }'
Explanation:
for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++): A loop that runs from 1 to 10.print "5 x", i, "=", 5 * i: Prints the multiplication table.

Example 4: Factorial Calculation
To calculate the factorial of a number (e.g., 5):
awk 'BEGIN { n = 5; factorial = 1; for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) factorial *= i; print "Factorial of", n, "is", factorial }'
Explanation:
n = 5: The number for which the factorial is calculated.factorial *= i: Multiplies the current value of factorial byiin each iteration.

Example 5: Summing Even Numbers
To sum only the even numbers from a file:
awk '{ if ($1 % 2 == 0) sum += $1 } END { print "Sum of Even Numbers:", sum }' numbers.txt
Explanation:
if ($1 % 2 == 0): Checks if the number is even.sum += $1: Adds the even number to the sum.

Conclusion
The awk command is a versatile tool for performing arithmetic operations in loops. By combining loops, conditions, and arithmetic operators, you can handle a wide range of tasks efficiently.
Practice these examples and experiment with your own scripts to unlock the full potential of awk!
