Ghost is a free and open-source blogging platform built with Node.js. As a fast, modern WordPress alternative, Ghost is focused completely on professional publishing. If you only want to publish content on the web and don’t need the additional features offered by WordPress, then Ghost is a great choice.
In this post, we will discuss how to install Ghost using RunCloud.
Let’s get started!
Create A New User
Ghost CLI needs sudo privileges, so instead of running your site as a root user, we recommend creating a new user with these sudo privileges. This can be done by running commands in the terminal, but it’s much easier to do within the RunCloud dashboard.
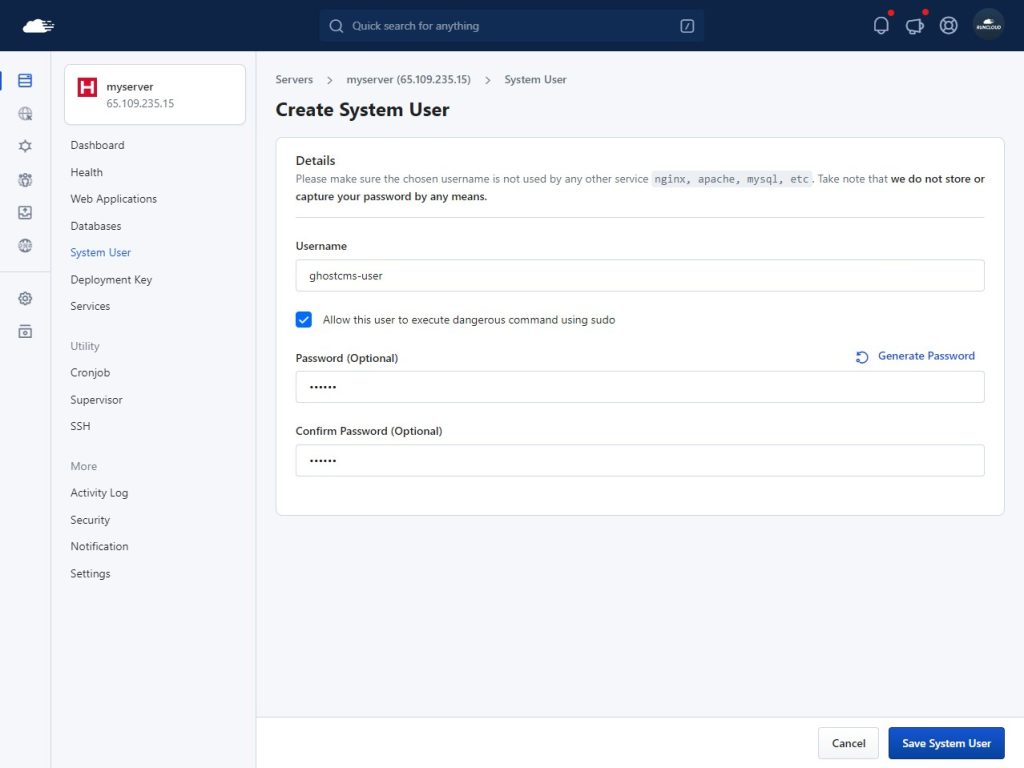
To create a new user, go to the RunCloud dashboard and open the “System User” menu.
Once opened, click “Add New System User” to create a new user. Give it a descriptive name and a secure password. Make sure to check the box to allow the execution of privileged commands.After this, click “Save System User” and continue the installation process.
Create A New Database
After creating the system user, the next step is to create a new database and database user. To do this, go to the “Database” menu under your server in the RunCloud Dashboard to create a new database user. Give this database user a suitable name and a secure password, and note these credentials, as they will be needed later during the installation.
After creating the database user, create a new database and grant permission to the user we just created. Save the changes before proceeding to the next step.

Create An Empty Web App
After you have created the user, go to the “Web Applications” tab and create a new web application on your server.
Choose the “Empty Web App” option and give your application a suitable name. Don’t forget to change the application’s owner. Instead of using the default RunCloud user, we will create the user account we just created as the owner of the web application.

After configuring the application owner, you can manually set up the domain and configure the DNS records on your DNS registrar’s site.
If you are using RunCloud’s Cloudflare integration, you can take advantage of the automatic DNS update functionality.
It is also possible to install Ghost using RunCloud’s test domain. If you want to follow this tutorial without setting up your domain or subdomain, use the RunCloud test domain.
For “Web Application Stack”, we recommend choosing “Native Nginx + Custom Config” to install Ghost CMS and then clicking “Deploy” to finish the set-up process.
If your server runs on OpenLiteSpeed, we’ve included notes on different steps in this guide.

After creating the app, go to the settings page and scroll down to the “Linked Database” section. From the dropdown menu, select the database we just created. Remember to click “Update Linked Database” to save the changes.

Installing Ghost-CLI (for Nginx and OLS servers)
Note: If you want to install GhostCMS on a Docker server, skip this section and jump to the Docker installation instructions.
In the previous step, we created a dummy web application in the RunCloud dashboard, which helps us perform administrative tasks such as monitoring the logs from the RunCloud dashboard. Now, we will use Ghost-CLI, a command-line tool, to install and configure Ghost CMS and replace that dummy application.
To avoid permission conflicts, we will install the Ghost-CLI as the web application’s owner. To do this, log in to your server as the system user assigned to the web application – you can either do this via SSH or use the su (switch user) command.
# Method 1
ssh ghostcms-user@<youripaddress>
# Method 2
ssh root@<youripaddress>
sudo su ghostcms-userAfter logging in to the server, navigate to the root directory of your web application using the following command. Replace the “<path to root>” with your path – you can find this in the RunCloud dashboard:
cd <path to root>Once in the correct directory, you can run the following commands to remove the default “index.html” file and begin the installation:
rm index.html
sudo npm install ghost-cli@latest -g
After the installation is complete, you can run “ghost version” on your terminal to check the version of Ghost-CLI and ensure that the CLI works as expected.

Checking Node.js version
Ghost CMS needs Node.js to function properly. At the time of writing, the recommended node version was 18; refer to the official website to see the recommended node version.
Execute the following command to see the version of the node installed on your server:
node -v
In the above screenshot, the first number in v18.18.0 indicates the major version number of the software. The major version number reflects the software’s level of compatibility and functionality. The other numbers after the dot (.) are minor version numbers or patch numbers. They do not affect the compatibility or functionality of the software as much as the major version number. Therefore, they can be ignored if you are only interested in the major version number.
Note: If you created your server before 27 September 2023, you might need to update the node version manually. Refer to our guide for updating the node on your RunCloud server to learn how to do this.
Installing Ghost CMS
After installing Ghost-CLI, you can run the following command to start the Ghost CMS installation:
ghost installDuring the installation, follow the instructions on the screen and enter the necessary information to proceed.
When asked for the hostname, enter 127.0.0.1. Using the default value causes the Ghost CMS to use the IPv6 address, which leads to an ECONNREFUSED::1:3306 error at a later stage in the installation.
When asked, “Do you wish to set up Systemd?” please enter “Y”, and when prompted, “Do you wish to start Ghost”, enter “Y” again.

If you follow the instructions correctly you will get a message that the installation was successful. However, when you visit your site you will see a 404 error message. This is because we skipped the Nginx setup during installation. We can configure this manually to fix it.
Before we set up the server proxy, we need to know which port Ghost will use for this website. Run the following command to get the details of your web application:
ghost ls The above command will show an output that looks like this:

In the example above, the port number is 2368. Note down this port number.
Installation on Docker
In addition to installing Ghost directly on an NGINX or OpenLiteSpeed server, you can also deploy Ghost using Docker. This allows you to take advantage of the consistency and portability of containerized applications.
To deploy Ghost on a Docker server, you must first set up an empty web application on your RunCloud server by following the steps described above. Once that is done, follow these steps:
- Log in to the server via SSH: Connect to your RunCloud server using SSH to access the terminal and run Docker commands.
- Create a Docker Compose file: Create a docker-compose.yml file that defines the Ghost container. This file should include the necessary environment variables for your database connection and the URL for your Ghost installation.
Here’s an example docker-compose.yml file:
services:
ghost:
image: ghost:5-alpine
restart: always
ports:
- 8080:2368
environment:
database__client: mysql
database__connection__host: host
database__connection__user: ghost_user
database__connection__password: asd123456
database__connection__database: ghost_db
url: http://ghost.example.com
volumes:
- ghost:/var/lib/ghost/content
extra_hosts:
- 'host:host-gateway'
volumes:
ghost:- Modify Dockerfile: After creating the above file, you must edit certain sections to ensure your application runs correctly. First, if deploying more than one Ghost container, you must replace
8080with a unique port number for each container. Next, you must replacehttp://ghost.example.comwith the URL of the web application you deployed earlier. - Create a custom NGINX proxy: Next, create a custom NGINX proxy for your RunCloud app to the custom port you defined in the Docker Compose file (in this case,
8080). You can use the same NGINX configuration as you would for a Ghost non-Docker installation (described below in this tutorial). - Start the Docker container: Finally, run
docker-compose up -din the directory containing thedocker-compose.ymlfile to start the Ghost container.
Setting Up A Proxy
You need to configure your server to redirect all the incoming traffic to the given port. This step is different for Nginx and OpenLiteSpeed servers. If you are not sure which server is installed on your machine, you can check this in the RunCloud dashboard and then follow along the instructions corresponding to your server.

For Nginx
Return to the RunCloud dashboard, open your web application, and go to the Nginx Config menu. Click the “Create Config” button and follow the steps below.
- For the “Type” option, select the value “location.root”.
- For the “Config Name” option, you can use the value “ghost”.
- Copy and paste the text below into the “ConfigContent” text area. Make sure to change X
XXXto the port number we noted earlier:
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:XXXX;
You can click “Run and Debug” to see if this custom config has any issues. Then, click the “Add Config” button to finish it.
For OpenLiteSpeed
In the RunCloud dashboard, open the empty web application created in the Create An Empty Web App step and look for the “LiteSpeed Config” in the side menu to open the configuration file.

We need to edit a few lines in this file. Firstly, note down the name of the extprocessor – we will use this later.
Next, disable the existing configuration by adding # before the type and address line.
After that, add the following lines below the commented lines. Don’t forget to change xxxx to the port number we noted earlier.
type proxy
address localhost:xxxxAt this stage, your configuration file should look like this:

Next, scroll down and add the following code snippet to your configuration file. Be careful not to paste it in the middle of an existing config block. Replace the <my-ghost> with the name of the extprocessor that we noted down earlier.
context / {
type proxy
handler <my-ghost>
addDefaultCharset off
}At this point, your config file will look something like this:

Click on “Update Config” to save the settings.
Finally, we need to restart the OpenLiteSpeed service for the changes to take effect. Open the server page in your RunCloud dashboard and look for the “Services” option in the side menu. On that page, click the “…” button next to the OpenLiteSpeed server and “Restart”.

Log In To Your Ghost Dashboard
After setting up the proxy config, you can visit your website. To configure the admin account, go to https://example.com/ghost. You must enter basic details on this page, such as the site name and admin login details.

After setting up the admin account, you can log into the Ghost dashboard and start publishing.

After Action Report
Ghost CMS is an effective modern publishing platform powered by Node.js. RunCloud makes it easy to install and configure Ghost CMS. After following the steps mentioned in this article, you will be able to set up your own CMS and start publishing content.
After installation, you can learn more about Ghost-CLI commands and tutorials to customize your Ghost blog.I
f you’re tired of managing your own servers, check out RunCloud, a simple yet powerful control panel for cloud servers. RunCloud is built for developers who want to focus on shipping great work, not on managing their infrastructure. Discover painless server configuration and say goodbye to spending hours figuring it out – get started with RunCloud today to get up and running in minutes.
Ghost Installation FAQs
What is Ghost blog, and why should I use it?
Ghost is a free and open-source blogging platform designed to be simple, elegant, and focused on writing. It is a great choice for users who want to create a professional-looking blog without the complexities of traditional content management systems such as WordPress.
What are the requirements for installing Ghost?
To install Ghost, you will need a web server running either NGINX or OpenLiteSpeed, Node.js, MySQL, or SQLite. You will also need to configure your server’s domain name and SSL/TLS certificate.
How do I install Ghost on an NGINX server?
To install Ghost on an NGINX server, you must first install Node.js and MySQL, then download and install the Ghost NPM package. Next, you will need to configure NGINX to serve the Ghost application and set up the database connection. Finally, you will need to start the Ghost service and configure any additional settings.
How do I install Ghost on an OpenLiteSpeed server?
Installing Ghost on an OpenLiteSpeed server is similar to the NGINX process but with a few key differences. First, you must install Node.js and MySQL, then download and extract the Ghost files. Next, you will need to configure OpenLiteSpeed to serve the Ghost application and set up the database connection. Finally, you will need to start the Ghost service and configure any additional settings.
What are some common issues that can arise when installing Ghost?
Some common issues that can arise when installing Ghost include problems with the Node.js or MySQL installation, difficulty configuring the web server, and issues with the database connection. It’s important to carefully follow the installation instructions and troubleshoot any errors.
How do I customize the appearance of my Ghost blog?
Ghost offers a wide range of themes and customization options, allowing you to easily change the look and feel of your blog. You can install pre-built themes or create custom themes using Ghost’s theme development tools.
What are the best practices for securing a Ghost blog?
To secure your Ghost blog, keep your software up-to-date, use strong passwords, and configure your web server with appropriate security settings. You should also consider enabling two-factor authentication and monitoring your blog for suspicious activity.
How do I integrate my Ghost blog with other tools and services?
Ghost offers many integrations, allowing you to connect your blog to other tools and services, such as social media platforms, email marketing providers, and analytics tools. You can also use Ghost’s API to build custom integrations and extend your blog’s functionality.
