Microsoft has released security updates for 85 vulnerabilities in its August 2024 Patch Tuesday rollout. These include six actively exploited zero-days (CVE-2024-38213, CVE-2024-38193, CVE-2024-38189, CVE-2024-38178, CVE-2024-38107, CVE-2024-38106). Among the updates is a fix for one of the vulnerabilities related to a ‘downgrade’ attack (CVE-2024-21302). Six of the vulnerabilities are rated Critical in severity, while the remaining 79 are rated Important or Moderate.
August 2024 Risk Analysis
This month’s leading risk type is elevation of privilege (37%) followed by remote code execution (35%) and information disclosure (8%).
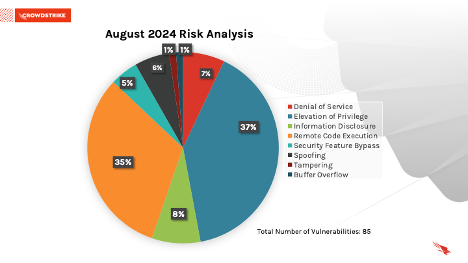
Figure 1. Breakdown of August 2024 Patch Tuesday attack types
Windows products received the most patches this month with 43, followed by Extended Security Update (ESU) with 21 and Microsoft Office with 8.

Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by August 2024 Patch Tuesday
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability in Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project received a patch for CVE-2024-38189, which has a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 8.8. This vulnerability allows an attacker to perform remote code execution by convincing a victim to click a link or open a malicious file. Microsoft advises customers to block macros from running in Office products and enable notifications.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 8.8 | CVE-2024-38189 | Microsoft Project Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Table 1. Zero-day in Microsoft Project
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities in Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock received a patch for CVE-2024-38193, with a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 7.8. These elevation of privilege vulnerabilities allow an attacker with low-level authentication to elevate access to obtain SYSTEM privileges. Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock is primarily responsible for handling network-related functions. Typically, these kinds of vulnerabilities are chained with remote code execution vulnerabilities to compromise systems. Details of the vulnerability, including the proof of concept for exploiting it, have not been publicly disclosed by Microsoft.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2024-38193 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Table 2. Zero-days in Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock and Windows Power Dependency Coordinator
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerabilities in Windows Power Dependency Coordinator
Windows Power Dependency Coordinator received a patch for CVE-2024-38107, with a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 7.8. This elevation of privilege vulnerability allows an attacker with low-level authentication to elevate access to obtain SYSTEM privileges. The attack is focused on the management of power states like sleep and wake functions in Windows. Typically, these kinds of vulnerabilities are chained with remote code execution vulnerabilities to compromise systems. Details of the vulnerability, including the proof of concept for exploiting it, have not been publicly disclosed by Microsoft.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2024-38107 | Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Table 3. Zero-days in Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock and Windows Power Dependency Coordinator
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability in Scripting Engine
Scripting Engine received a patch for CVE-2024-38178, which has a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 7.5. This vulnerability requires an authenticated user to be using Edge in Internet Explorer mode and clicking on a compromised URL. This allows an unauthenticated attacker to initiate remote code execution.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.5 | CVE-2024-38178 | Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability |
Table 4. Zero-day in Scripting Engine
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability in Windows Kernel
The Windows kernel received a patch for CVE-2024-38106, which has a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 7.0. This is an elevation of privilege vulnerability that leads to SYSTEM privileges. This attack is highly complex and requires the attacker to win a race condition; however, some race conditions may be easier than others. Details of the vulnerability, including a proof of concept, have not been publicly disclosed by Microsoft.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.0 | CVE-2024-38106 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Table 5. Zero-day in the Windows kernel
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability in Windows Mark of the Web Security
Windows Mark of the Web Security received a patch for CVE-2024-38213, which has a severity of Important and a CVSS score of 6.5. A vulnerability in the Windows Defender SmartScreen allows an attacker to bypass security warnings when a malicious file is downloaded. This security feature has been bypassed multiple times over the years (March 2023, July 2023, November 2023, February 2024), making it a prime target for threat actors utilizing it in phishing attacks.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Moderate | 6.5 | CVE-2024-38213 | Windows Mark of the Web Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Table 6. Zero-day in Windows Mark of the Web Security
Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Network Virtualization, TCP/IP, Reliable Multicast Transport Driver, Azure Health Bot and Secure Boot
CVE-2024-38063 is a Critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Windows TCP/IP and has a CVSS score of 9.8. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows an attacker to execute code remotely. Microsoft has not provided other details but suggests disabling IPv6 as only IPv6 packets can be abused to exploit this vulnerability. The attack complexity is low, and exploitation is more likely, per Microsoft.
CVE-2024-38140 is a Critical RCE vulnerability affecting Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) and has a CVSS score of 9.8. The vulnerability is only exploitable if there is a program listening on a Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) port. If PGM is installed or enabled, but no active software is listening, then this vulnerability is not exploitable. Most organizations have controls (e.g., a firewall) in place to protect access to any ports at the network level.
CVE-2024-38109 is a Critical elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Azure Health Bot and has a CVSS score of 9.1. This vulnerability allows an attacker to access Azure’s internal metadata service (IMDS) by utilizing server-side request forgery (SSRF). Successfully exploiting this vulnerability allows the attacker to gain elevated privileges over the network.
CVE-2024-38159 and CVE-2024-38160 are Critical RCE vulnerabilities affecting Windows Network Virtualization, and both have a CVSS score of 9.1. Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow the attacker to interact with other tenants’ applications and content. This can only be achieved with a high level of control over the machine. Microsoft has provided mitigation factors in order to successfully secure virtual machines, such as the importance of Hyper-V on virtualization infrastructures.
CVE-2023-40547 is a Critical RCE vulnerability affecting Secure Boot and has a CVSS score of 8.8. Microsoft has included this vulnerability as it has been heavily involved in developing and implementing a security standard in Secure Boot. Secure Boot is designed to prevent unauthorized code from running during the boot process by ensuring that only software signed by trusted keys is executed. This particular vulnerability poses a risk to the integrity of Secure Boot and Microsoft will apply a Secure Boot Advanced Targeting (SBAT) update to block vulnerable Linux boot loaders that could impact Windows security.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2024-38063 | Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2024-38140 | Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.1 | CVE-2024-38109 | Azure Health Bot Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.1 | CVE-2024-38159 | Windows Network Virtualization Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.1 | CVE-2024-38160 | Windows Network Virtualization Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.8 | CVE-2023-40547 | Redhat: CVE-2023-40547 Shim – RCE in HTTP boot support may lead to secure boot bypass |
Table 7. Critical vulnerabilities in Windows and Azure
Vulnerabilities with Existing Proof of Concept in Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) Service, Windows Update Stack and Windows Secure Kernel Mode
CVE-2024-38199 is an Important RCE vulnerability affecting Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) and has a CVSS score of 9.8. An unauthenticated attacker sending specially crafted print tasks to a shared vulnerable Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) service could result in remote code execution. The good news is that Microsoft has deprecated LPD since Windows Server 2012, and it is not installed or enabled by default.
CVE-2024-38202 is an Important elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Windows Update Stack and has a CVSS score of 7.3. Microsoft was notified of an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Backup. This vulnerability could potentially enable an attacker with basic user privileges to reintroduce previously patched vulnerabilities or circumvent some features of virtualization-based security (VBS).
While there have been no known attempts to exploit these vulnerabilities in the wild, a public presentation at Black Hat last week (“Windows Downdate: Downgrade Attacks Using Windows Updates” by SafeBreach) showcased their use in a vulnerability chain in order to compromise a system. Due to the complexity of the attack, there are no security updates to mitigate this threat as of yet. Microsoft has issued an advisory with recommended actions to help reduce the risk of exploitation until the security update is available.
CVE-2024-21302 is an Important elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Windows Secure Kernel Mode and has a CVSS score of 6.7. Microsoft was notified of a secure kernel mode elevation vulnerability in Windows-based systems supporting VBS. This vulnerability could enable an attacker with administrator privileges to replace current versions of Windows system files with outdated versions. While there have been no known attempts to exploit this vulnerability in the wild, the same Black Hat presentation mentioned above showcased its use in a vulnerability chain in order to compromise a system. Microsoft has released a security update that includes opt-in revocation policy mitigations to address this vulnerability. Microsoft encourages customers running affected versions of Windows to review the advisory and knowledge base.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 9.8 | CVE-2024-38199 | Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.3 | CVE-2024-38202 | Windows Update Stack Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 6.7 | CVE-2024-21302 | Windows Secure Kernel Mode Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Table 8. Vulnerabilities with existing proof of concept available in .NET, Visual Studio and ARM-based operating systems
Patch Tuesday Dashboard in the Falcon Platform
For a visual overview of the systems impacted by this month’s vulnerabilities, you can use our newly available Patch Tuesday dashboard. You can find it in the Falcon platform within the Exposure Management > Vulnerability Management > Dashboards page. The preset dashboards show the most recent three months of Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities.
Not All Relevant Vulnerabilities Have Patches: Consider Mitigation Strategies
As we have learned with other notable vulnerabilities, such as Log4j, not every highly exploitable vulnerability can be easily patched. As is the case for the ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities, it’s critically important to develop a response plan for how to defend your environments when no patching protocol exists.
Regular review of your patching strategy should still be a part of your program, but you should also look more holistically at your organization’s methods for cybersecurity and improve your overall security posture.
The CrowdStrike Falcon® platform regularly collects and analyzes trillions of endpoint events every day from millions of sensors deployed across 176 countries. Watch this demo to see the Falcon platform in action.
Learn More
Learn more about how CrowdStrike Falcon® Exposure Management can help you quickly and easily discover and prioritize vulnerabilities and other types of exposures here.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- For more information on which products are in Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates program, refer to the vendor guidance here.
- See how Falcon Exposure Management can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities and other exposures in your environments.
- Learn how CrowdStrike’s external attack surface module, CrowdStrike® Falcon Surface™, can discover unknown, exposed and vulnerable internet-facing assets, enabling security teams to stop adversaries in their tracks.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen antivirus for yourself with a free trial of CrowdStrike® Falcon Prevent™.
